Dear Aspirants, Quantitative Aptitude plays a crucial role in Banking and all other competitive exams. To enrich your preparation, here we have provided New Pattern Aptitude Questions that are similar to the questions asked in IBPS PO Mains 2018. Candidates those who are going to appear in upcoming bank exams like IBPS Clerk, IBPS SO, etc., can practice these questions daily and make your preparation effective.
[WpProQuiz 4532]Directions (Q. 1 – 5): The questions below are based on the given Series-I. The series-I satisfy a certain pattern, follow the same pattern in Series-II and answer the questions given below.
1)
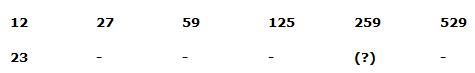
a) 427
b) 463
c) 435
d) 297
e) 623
2)
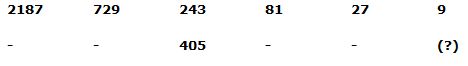
a) 18
b) 15
c) 16
d) 12
e) 21
3)
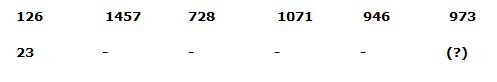
a) 961
b) 689
c) 790
d) 870
e) 890
4)
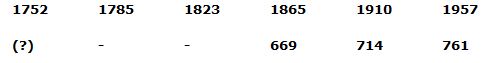
a) 556
b) 456
c) 486
d) 526
e) 429
5)
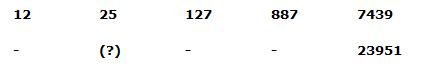
a) 121
b) 119
c) 113
d) 117
e) 111
Directions (6 – 10): Study the following graph carefully and answer the given questions.
The table shows the discount rate of four different items in five different shops.
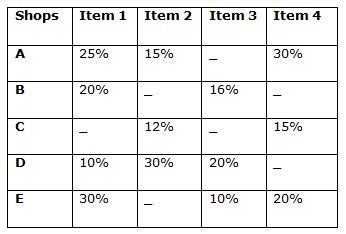
Note: Selling price for each item is same in all the shops
6) Quantity I: If the ratio of the marked price of item 1 and item 4 in shop E is 15: 14, and the marked price of shop D in item 1 is Rs. 7000. Find the selling price of item 4 in shop E?
Quantity II: In item 2, if marked price in shop C is 25% more than the cost price and the profit percentage of shop C is 10% which is equal to 280. Find the cost price of shop D if marked price of item 2 in shop D is 10% more than the cost price?
a) Quantity I > Quantity II
b) Quantity I ≥ Quantity II
c) Quantity I < Quantity II
d) Quantity I ≤ Quantity II
e) Quantity I = Quantity II (or) Relationship cannot be determined
7) Quantity I: Item 3, cost price of all the shops is Rs. 4800 and the marked price is 40%, 50% and 25% more than the cost price in shop B, D and E respectively. Find the total selling price of shop B, D and E together
Quantity II: If the selling price of item 4 of all the shops is Rs. 9520, find the total marked price of shop A, C and E?
a) Quantity I > Quantity II
b) Quantity I ≥ Quantity II
c) Quantity I < Quantity II
d) Quantity I ≤ Quantity II
e) Quantity I = Quantity II (or) Relationship cannot be determined
8) Quantity I: In shop E, Cost price of item 1 is Rs. 800 more than the cost price of item 4 and the marked price of item 1 and 4 is 60 % and 40 % more than the cost price respectively. Find the selling price of item 4 if the selling price is same for both the items?
Quantity II: If the marked price of item 3 in shop B is 20% more than the cost price, which is 6000, find the marked price of item 3 in shop D?
a) Quantity I > Quantity II
b) Quantity I ≥ Quantity II
c) Quantity I < Quantity II
d) Quantity I ≤ Quantity II
e) Quantity I = Quantity II (or) Relationship cannot be determined
9) In shop D, if the ratio of marked price in item 1, item 2 and item 3 is 56: 72: 63 and the marked price of item 1 in shop B is Rs.6300.
Quantity I: Find the marked price of item 2 in shop A
Quantity II: Find the marked price of item 3 in shop E
a) Quantity I > Quantity II
b) Quantity I ≥ Quantity II
c) Quantity I < Quantity II
d) Quantity I ≤ Quantity II
e) Quantity I = Quantity II (or) Relationship cannot be determined
10) Quantity I: Find the marked price of item 4 in shop A. If the marked price of item 4 in shop E is Rs. 6300
Quantity II: Find the marked price of item 2 in shop C. If the marked price of item 2 in shop D is Rs. 4400
a) Quantity I > Quantity II
b) Quantity I ≥ Quantity II
c) Quantity I < Quantity II
d) Quantity I ≤ Quantity II
e) Quantity I = Quantity II (or) Relationship cannot be determined
Answers:
Directions (1-5):
1) Answer: c)
Series I pattern:
12*2 + 3 = 27
27*2 + 5 = 59
59*2 + 7 = 125
125*2 + 9 = 259
259*2 + 11 = 529
Series II pattern:
23*2 + 3 = 49
49*2 + 5 = 103
103*2 + 7 = 213
213*2 + 9 = 435
435*2 + 11 = 881
The answer is, 435
2) Answer: b)
Series I pattern:
2187 ÷ 3 = 729
729 ÷ 3 = 243
243 ÷ 3 = 81
81 ÷ 3 = 27
27 ÷ 3 = 9
Series II pattern:
3645 ÷ 3 = 1215
1215 ÷ 3 = 405
405 ÷ 3 = 135
135 ÷ 3 = 45
45 ÷ 3 = 15
The answer is, 15
3) Answer: d)
Series I pattern:
126 + 113 = 1457
1457 – 93 = 728
728 + 73 = 1071
1071 – 53 = 946
946 + 33 = 973
Series II pattern:
23 + 113 = 1354
1354 – 93 = 625
625 + 73 = 968
968 – 53 = 843
843 + 33 = 870
The answer is, 870
4) Answer: a)
Series I pattern:

Series II pattern:
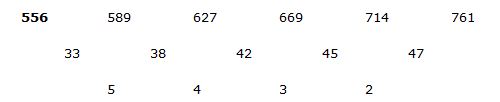
The answer is, 556
5) Answer: e)
Series I pattern:
12*2 + 13 = 25
25*4 + 33 = 127
127*6 + 53 = 887
887*8 + 73 = 7439
Series II pattern:
55*2 + 13 = 111
111*4 + 33 = 471
471*6 + 53 = 2951
2951*8 + 73 = 23951
The answer is, 111
Directions (6-10):
6) Answer: a)
Quantity I: If the ratio of the marked price of item 1 and item 4 in shop E is 15: 14, and the marked price of shop D in item 1 is Rs. 7000. Find the selling price of item 4 in shop E?
Selling price of item 1 in shop D = 7000 * [(100 – 10)/100]
= > 7000*(90/100) = Rs. 6300
Marked price of item 1 in shop E = [6300/(100-30)]*100
= > 6300/70 * 100 = 9000
Marked price of item 4 in shop E = 9000 * (14/15) = 8400
Selling price of item 4 in shop E = 8400 * [(100-20)/100]
= > 8400 * 80/100 = Rs. 6720
Quantity II: In item 2, if marked price in shop C is 25% more than the cost price and the profit percentage of shop C is 10% which is equal to 280. Find the cost price of shop D if marked price of item 2 in shop D is 10% more than the cost price?
Profit of item 2 in shop C = Rs. 280 = 10% of cost price of item 2 in shop C
Cost price of item 2 in shop C = 280*(100/10) = 2800
Marked price of item 2 in shop C = 2800 * [(100 + 25)/100]
= > 2800 * 125/100 = 3500
Selling price of item 2 in shop C = 3500 * (100 – 12)/100
= > 3500 * (88/100) = Rs. 3080
Marked price of item 2 in shop D = 3080 * (100/(100-30))
= > (3080/70)*100= 4400
Cost price of item 2 in shop D = (4400/110)*100 = Rs. 4000
Quantity I > Quantity II
7) Answer: c)
Quantity I: Item 3, cost price of all the shops is Rs. 4800 and the marked price is 40%, 50% and 25% more than the cost price in shop B, D and E respectively. Find the total selling price of shop B, D and E together
Marked price of item 3 in shop B = 4800 * (140/100) = 6720
Marked price of item 3 in shop D =4800*(150/100) = 7200
Marked price of item 3 in shop E =4800* (125/100) = 6000
Selling price of item 3 in shop B = 6720 * [(100-16)/100] = 5644.8
Selling price of item 3 in shop D = 7200 * [(100-20)/100] =5760
Selling price of item 3 in shop E = 6000 * [(100-10)/100] = 5400
Required total = (5644.8 + 5760 + 5400) = Rs. 16804.4
Quantity II: If the selling price of item 4 is Rs.9520, find the total marked price of shop A, C and E
Marked price of item 4 in shop A = 9520 * (100/70) = 13600
Marked price of item 4 in shop C = 9520 *(100/85) = 11200
Marked price of item 4 in shop E = 9520 * (100/80) = 11900
Required total = (13600+11200+11900) = Rs. 36700
Quantity I < Quantity II
8) Answer: c)
Quantity I: In shop E, Cost price of item 1 is 800 more than the cost price of item 4 and the marked price of item 1 and 4 is 60 % and 80 % more than the cost price respectively. Find the selling price of item 4 if the selling price is same for both the items?
Cost price of item 4 in shop E = x
Cost price of item 1 in shop E = x+800
Marked price of item 1 in shop E = (x+800) * [(100+60)/100]
=> (x + 800)*(160/100) = (x + 800)*(8/5) = (8x + 6400)/5
Marked price of item 4 in shop E = x * (100 + 80)/100
= > (x)*(180/100)
Selling price of item 1 in shop E = (2x+1600) * [(100-30)/100]
= > [(8x + 6400)/5] * 70/100
= > [(8x + 6400)/5]*(7/10)
Selling price of item 4 in shop E = (x) * (180/100) * [(100-20)/100]
= > (x) * (180/100) * (4/5)
= > 36x/25
According to the question,
Selling price of both the items is same
[(8x + 6400)/5]*(7/10) = 36x/25
56x + (6400*7) = 72x
16x = (6400*7)
X = 2800
Selling price of item 4 in shop E = 36x/25 = (36/25)*2800 = Rs. 4032
Quantity II: If the marked price of item 3 in shop B is 20% more than the cost price, which is 6000, find the marked price of item 3 in shop D
Cost price of item 3 in shop B = 6000
Marked price of item 3 in shop B = 6000 * 120/100 = 7200
Selling price of item 3 in shop B = 7200 * [(100-16)/100]
= > 7200*(84/100) = 6048
Marked price of item 3 in shop D = 6048 * (100/80) = Rs. 7560
Quantity I < Quantity II
9) Answer: a)
In shop D, if the ratio of marked price in item 1, item 2 and item 3 is 56: 72: 63 and the marked price of item 1 in shop B is Rs. 6300.
Selling price of item 1 in shop B = 6300 * (100-20)/100
=> 6300 * 80/100 = 5040
Marked price of item 1 in shop D = 5040 *(100/100-10)
=> 5040 * 100/90 = 5600
Marked price of item 2 in shop D = 5040 * (100/100-30)
= > 5040 *(100/70) = 7200
Marked price of item 3 in shop D = 5040 * (100/100-20)
= > 5040 * (100/80) = 6300
Quantity I: Find the marked price of item 2 in shop A
Selling price of item 2 in shop D = 7200 * [(100 – 30)/100]
=> 7200 * (70/100) = 5040
Marked price of item 2 in shop A = 5040 * (100/85) = Rs. 5929.4
Quantity II: Find the marked price of item 3 in shop E
Selling price of item 3 in shop D = 6300 * (100-20)/100
= > 6300 * (80/100) = 5040
Marked price of item 3 in shop E = 5040 * (100/90) = Rs. 5600
Quantity I > Quantity II
10) Answer: a)
Quantity I: Find the marked price of item 4 in shop A. If the marked price of item 4 in shop E is Rs. 6300
Selling price of item 4 in shop E = 6300 * (100 – 20)/100
= > 6300 * 80/100 = 5040
Marked price of item 4 in shop A = 5040 * (100/70) = Rs. 7200
Quantity II: Find the marked price of item 2 in shop C. If the marked price of item 2 in shop D is Rs.4400
Selling price of item 2 in shop D = 4400 * (100-30)/100
=> 4400 * 70/100 = 3080
Marked price of item 2 in shop C = 3080 * (100/88) = Rs. 3500
Quantity I > Quantity II





