Dear Aspirants, Our IBPS Guide team is providing new series of Quantitative Aptitude Questions for IBPS RRB Clerk Mains 2019 so the aspirants can practice it on a daily basis. These questions are framed by our skilled experts after understanding your needs thoroughly. Aspirants can practice these new series questions daily to familiarize with the exact exam pattern and make your preparation effective.
Check here for IBPS RRB PO Mains Mock Test 2019
Check here for IBPS RRB Clerk Mains Mock Test 2019
Check here for IBPS PO Prelims Mock Test 2019
Click Here to Subscribe Crack High Level Puzzles & Seating Arrangement Questions PDF 2019 Plan
[WpProQuiz 7113]Directions (1 – 5): The table shows the discount % given by stores on different items. The market price of any article on all stores is same. Some values are missing. Answer the questions on the basis of given table and information in question.
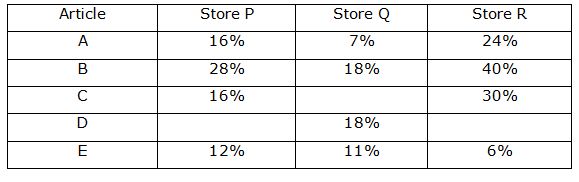
1) If the average SP of article B in all the stores is Rs.2568, Find the MP of article B?
a) 1100
b) 1200
c) 1500
d) 2000
e) None of these
2) Difference between SP of article A by stores P and Q is Rs.486, Find the SP of same article by store R.
a) 3806
b) 4000
c) 4100
d) 4104
e) None of these
3) Average SP of article C by stores P and Q is Rs.3608, by stores Q and R is Rs.3300. Find the SP of article C by store R.
a) 3080
b) 3000
c) 3100
d) 3200
e) None of these
4) Store P earned 10% profit by selling product E. If CP of articles at all articles is same, Find the ratio of profits by Q and R in selling E.
a) 14:9
b) 3:7
c) 9:14
d) 7:15
e) None of these
5) Ratio of discounts on article D by stores P and Q is 2/3. Difference in SP of article D by stores P and R is Rs.432. If SP of article D by store P is Rs.216 more than that by store Q, find the SP of article D by store R?
a) 2690
b) 2800
c) 2720
d) 2750
e) None of these
Directions (6 – 10): Each question contains a statement followed by Quantity I and Quantity II. Read the contents clearly and answer your questions accordingly.
6) P and Q started a business with Rs.10000 and Rs.15000 respectively. After 6 months R joined them with Rs.20000.
Quantity I: Q′s share in total profit of Rs.4,00,000 at the end of 2 years.
Quantity II: Annual Salary of Akash after tax deduction if he earns Rs.20,000 per month and pays a tax of 20% each month.
a) Quantity I >Quantity II
b) Quantity I <Quantity II
c) Quantity I ≥Quantity II
d) Quantity I ≤Quantity II
e) Quantity I =Quantity II or No relation
7) M can do a work in 16 days. N is 60% more efficient than M.
Quantity I: Time taken by M and N together to do the work.
Quantity II: Time taken by M and N to do the work together when M works at doubles his original efficiency and N works at half his original efficiency.
a) Quantity I >Quantity II
b) Quantity I <Quantity II
c) Quantity I ≥Quantity II
d) Quantity I ≤Quantity II
e) Quantity I =Quantity II or No relation
8) A bag contains 3 Yellow, 4 black and 2 white balls. Two balls are drawn at random.
Quantity I: Probability that none of the ball drawn is white.
Quantity II: Fraction of work completed by P in 7 days if he is 20% more efficient than A who can complete the work in 12 days.
a) Quantity I >Quantity II
b) Quantity I <Quantity II
c) Quantity I ≥Quantity II
d) Quantity I ≤Quantity II
e) Quantity I =Quantity II or No relation
9) Sunny took a loan from bank at 12% P.A. simple interest. After 3 years he had to pay back Rs.16200 as interest.
Quantity I: Loan taken by Sunny from the bank.
Quantity II: Amount after 2 years for a principal of Rs.35,000 at interest rate of 10% compounded annually.
a) Quantity I >Quantity II
b) Quantity I <Quantity II
c) Quantity I ≥Quantity II
d) Quantity I ≤Quantity II
e) Quantity I =Quantity II or No relation
10) A person can row 9Kmph in still water. It takes him twice as long to row up as to row down the river.
Quantity I: Rate of stream.
Quantity II: Speed of a person in still water who can row upstream at 4kmph and downstream at 2kmph.
a) Quantity I >Quantity II
b) Quantity I <Quantity II
c) Quantity I ≥Quantity II
d) Quantity I ≤Quantity II
e) Quantity I =Quantity II or No relation
Answers :
Directions (1-5) :
1) Answer: b)
SP by store P = MP * (100-28)/100 = MP * 72%
By Q = 82% of MP,
By R = 60% of MP
(72 + 82 + 60) * MP/100 = 2568
214 * MP/100 =2568
MP= Rs.1200
2) Answer: d)
Difference in SP= 93% of MP – 84% of MP
9% of MP = 486
MP = 5400
SP by store Q = 76% of 5400 = Rs.4104
3) Answer: a)
Let x% discount by store Q
[84 + (100 – x)]/2 * 100 * MP = 3608………(i)And [70 + (100 – x)]/2 * 100 * MP = 3300……..(ii)
Put value of (100-x) from equation (i) to (ii) and solve
MP = Rs.4400
SP by store R = 4400 * 70/100 = Rs.3080
4) Answer: c)
MP = x
SP by P = 88% of x
CP by P = x * 88/100 * 100/110 = 4x/5
Now CP is same
SP by Q = 89x/100
Profit of Q = 89x/100 – 4x/5 = 9x/100
SP by R = 94x/100
Profit of Q = 94x/100 – 4x/5 = 14x/100
Required ratio = 9: 14
5) Answer: e)
x/18 = 2/3
Discount by P= 12%
Now, 88% of MP = 82% of MP +216
MP = Rs.3600
Now, let y% discount by store Q = [88 – (100 – y)]/100 *MP =432
MP = Rs.3600
Y = 24%
SP by R= 76% of 3600 = Rs.2736
Direction (6-10) :
6) Answer: b)
Quantity I: A: B: C = 10000*24 : 15000*24 : 20000*18=2:3:3
B=3/8 *400,000= Rs.150000
Quantity II: Salary after deduction = 20,000*12*80/100 = Rs.192000
Hence, Quantity I < Quantity II
7) Answer: a)
Quantity I: M =16 days; N = 16 * 100/160=10 days
M+N together = 16*10/(26)=80/13 days
Quantity II: M = 16 days; N = 10 days
M (double efficiency) = 8 day; A (half efficiency) = 20 days
M+N together = 80/14
Hence, Quantity I > Quantity II
8) Answer: b)
Quantity I: 7C2/9C2=7/12
Quantity II: A-> 10 days => fraction of work in 7 days = 7/10
Hence, Quantity I < Quantity II
9) Answer: a)
Quantity I: P=16200*100/(3*12)=Rs.45,000
Quantity II: A= 35000*121/100=Rs.42350
Hence, Quantity I > Quantity II
10) Answer: e)
Quantity I: 9+y=2(9-y)
y = 3kmph
Quantity II: x = (4+2)/2=3kmph
Hence Quantity I = Quantity II





