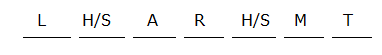Dear Aspirants, Our IBPS Guide team is providing new series of Reasoning Questions for IBPS RRB PO Mains 2019 so the aspirants can practice it on a daily basis. These questions are framed by our skilled experts after understanding your needs thoroughly. Aspirants can practice these new series questions daily to familiarize with the exact exam pattern and make your preparation effective.
Check here for IBPS RRB PO Mains Mock Test 2019
Check here for IBPS RRB Clerk Mains Mock Test 2019
Check here for IBPS PO Prelims Mock Test 2019
Click Here to Subscribe Crack High Level Puzzles & Seating Arrangement Questions PDF 2019 Plan
[WpProQuiz 6906]
Directions (1-3): In each of the following questions some statements are given followed by two conclusions numbered I and II. You have to take the given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance from commonly known facts.
Give answer if:
a) Only I follow
b) Only II follows
c) Either I or II follows
d) Neither I nor II follows
e) Both I & II follow
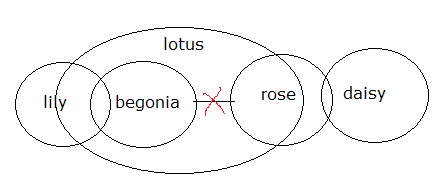
1) Statements:
Some lily are begonia
No begonia is rose
Some rose are daisy
All begonia re lotus
Some lotus are rose
Conclusions:
I) Some begonia are not daisy
II) All lily can be daisy
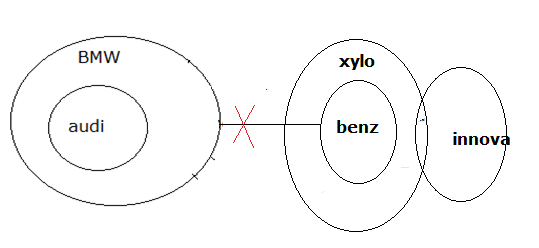
2) Statements:
All Audi are BMW
No BMW is benz
All Benz are Xylo
Some Xylo are Innova
Conclusions:
I) Some Innova are BMW
II) Only a few Xylo are Audi
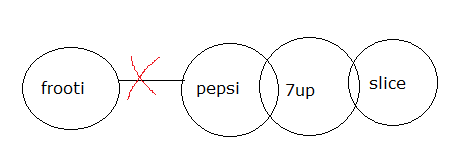
3) Statements:
No frooti is pepsi
Some pepsi are 7up
Some 7up are slice
Conclusions:
I) All slice can never be frooti
II) All frooti can be 7up
Directions (4-7): Study the following information carefully and answer the given questions.
A word and number arrangement machine when given an input line of words and numbers rearranges them following a particular rule in each step. The following is an illustration of input and rearrangement (All the numbers are two digits numbers)
Input: waivers 22 slump 31 invoices 58 72 money 43 13 occupy volatile
Step I: 14 waivers 22 slump 31 58 72 money 43 occupy volatile invoices
Step II: 21 14 waivers slump 31 58 72 money 43 volatile invoices occupy
Step III: 32 21 14 slump 58 72 money 43 volatile invoices occupy waivers
Step IV: 44 32 21 14 slump 58 72 money invoices occupy waivers volatile
Step V: 57 44 32 21 14 72 money invoices occupy waivers volatile slump
Step VI: 71 57 44 32 21 14 invoices occupy waivers volatile slump money
As per the rules followed in the steps given above, find out in each of the following questions the appropriate step for the given input.
Input: ample 78 shrill 48 export 90 curtain 97 fractious 51 gaffe 31
4) How many elements are there between ‘shrill’ and ‘51’ in step II?
a) Three
b) Four
c) Two
d) One
e) None of these
5) What is the average of third element from the left end in step IV and fifth from the right end in step I?
a) 60
b) 74
c) 69
d) 72
e) None of these
6) What is the difference between fourth element from the left end in step III and eighth from the right end in step VI?
a) 50
b) 37
c) 31
d) 51
e) None of these
7) What is the position of ‘curtain’ with respect to ‘ample’ in step II?
a) Fifth to the right
b) Fourth to the left
c) Fourth to the right
d) Fifth to the left
e) None of these
Directions (8-10): Each of the questions below consists of a question and two statements numbered I and II given below it. You have to decide whether the data given in the statements are sufficient to answer the question. Read both statement and choose the most appropriate option
a) Only Statement I is sufficient to answer
b) Only Statement II is sufficient to answer
c) Either Statement I or Statement II are sufficient to answer.
d) Neither Statement I nor Statement II are sufficient to answer.
e) Both Statement I and Statement II are sufficient to answer.
8) Six persons K, R, H, M,L and P attends the class in a week starting from Monday and ends on Saturday. Which of the following person attends the class immediately after P?
I) R attends the class before Wednesday. As many persons attend the class before R attends the class after M. L attends the class after M. More than three persons attend the class between L and H. K attends the class before P.
II) Two persons attend the class between M and R. H attends the class before R. As many persons attends the class before K attends the class after P.
9) Eight persons P, Q, R, S, T, V, L and M are sitting around a circular table facing centre. How many person sits between R and P, when counted from left of P?
I) T sits second to the left of R. Two persons sit between L and M. Neither L nor M is an immediate neighbour of R. V sits immediate left of Q.
II) Q sits third to the right of L. T and L are immediate neighbours. Only one person sits between P and S. P does not sit opposite to V.
10) Seven persons L, A, H, R, S, T and M are sitting in a row facing north. Who sits at extreme right end?
I) Two persons sit between H and S. More than three persons sit between L and M. L sits left of H. M does not sit at extreme end. Two persons sit between R and T. A sits immediate left of R.
II) S sits left of H. As many person sits to the left of S sits to the right of A. More than one person sits between T and R.
Answers :
Directions (1-3):
1) Answer : (b)
2) Answer : (d)
3) Answer : (b)
Directions (4-7):
Input: ample 78 shrill 48 export 90 curtain 97 fractious 51 gaffe 31
Step I: 32 78 shrill 48 export 90 curtain 97 fractious 51 gaffe ample
Step II: 47 32 78 shrill 90 curtain 97 fractious 51 gaffe ample export
Step III: 52 47 32 78 90 curtain 97 fractious gaffe ample export shrill
Step IV: 77 52 47 32 90 curtain 97 fractious ample export shrill gaffe
Step V: 89 77 52 47 32 curtain 97 ample export shrill gaffe fractious
Step VI: 98 89 77 52 47 32 ample export shrill gaffe fractious curtain
Numbers are arranged in descending order which is followed by vowel in ascending order which is followed by consonants in descending order in final step.
If a number is odd, then add+1 else -1.
4) Answer (b)
5) Answer : (d)
6) Answer : (c)
7) Answer : (d)
Directions (8-10):
8) Answer : (a)

9) Answer :(d)
neither options gives the answer. And with the help of both the options we can’t get the answer.
10) Answer : (a)