Important Computer Awareness Materials (Day-26) – Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) Model:
Dear Readers, IBPS Exams are approaching shortly, we all knew that Computer Awareness is one of the important section, which will help you to increase your score easily.
Many of our followers were asking us to provide Important Computer Awareness Notes along with the model questions, here we have planned to provide the Topic wise Important Computer Awareness Materials on Daily basis, and also we will provide MCQs based on these topics daily. Kindly follow us regularly and make use of it.
Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) Model
The Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model defines a networking framework to implement protocols in layers, with control passed from one layer to the next.
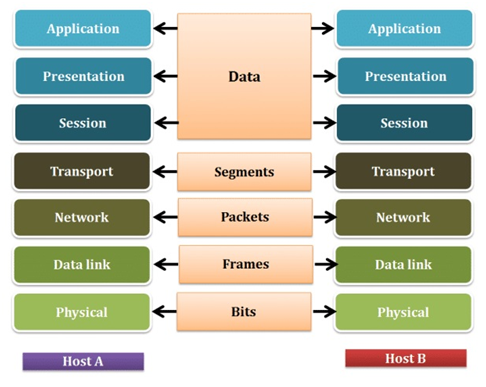
Layer 7: Application layer:
The application layer supplies network services to end-user applications. It provides services for the application program to ensure that effective communication with another application program in a network is possible.
Layer 6: Presentation layer:
It works as the translator for the network. This layer converts data from a format used by the application layer into a common format at the sending station and converts the common format to a format known to the application layer at the receiving station.
Layer 5: Session layer:
The session layer allows two application processes on different machines to establish, use and terminate a connection, called a session.
Layer 4: Transport layer:
The transport layer ensures that message delivery is error-free, in sequence, and with no losses or duplication. It relieves the higher layer protocols from any concern with the transfer of data between them and their peers.
Layer 3: Network layer:
The network layer provides data routing paths for network communication. Data is transferred in the form of packets via logical network paths in an ordered format that the network layer controls.
Layer 2: Data link layer:
This layer sets up links across the physical network, putting packets (structured bit stream) into network frames. This layer has two sub-layers, the Logical Link Control Layer and the Media Access Control Layer.
The Logical Link Control Layer (LLC) is concerned with managing traffic (flow and error control) over the physical medium.
The Media Access Control (MAC) layer is responsible for moving data packets to and from one Network Interface Card (NIC) to another across a shared channel.
Layer 1: Physical layer:
The physical layer, the lowest layer of the OSI model, is concerned with the transmission and reception of the unstructured raw bit stream over a physical medium. It provides the hardware means of sending and receiving data on a carrier network.
IPv4 and IPv6 – The Internet Protocols in OSI
IPv4 and IPv6 are different versions of the Internet Protocol – Internet Protocol version
4 (IPv4), Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6). IPv6 is also called IPng (Internet Protocol next generation)
Click Here for Computer Awareness Materials (Day-1 to Day-25)