Dear Aspirants, the most awaited notification of SBI PO – 2019 has been released. We all know that new pattern questions are introducing every year in the SBI PO exam. Further, the questions are getting tougher and beyond the level of the candidate’s expectations.
Our IBPS Guide is providing High-Level New Pattern Quantitative Aptitude Questions for SBI PO 2019 so the aspirants can practice it on a daily basis. These questions are framed by our skilled experts after understanding your needs thoroughly. Aspirants can practice these high-level questions daily to familiarize with the exact exam pattern. We wish that your rigorous preparation leads you to a successful target of becoming SBI PO.
“Be not afraid of growing slowly; be afraid only of standing still”
[WpProQuiz 6692]
Click Here to Take Free Mock Test For SBI PO Mains
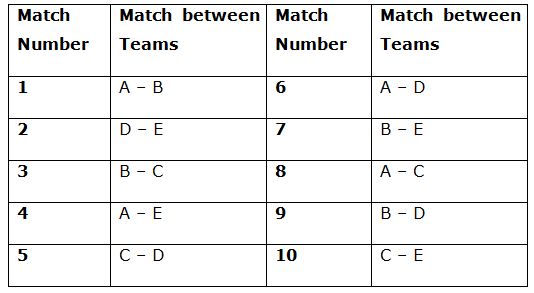
Direction (1 – 5): Study the following data carefully and answer the questions:
A cricket match tournament 5 teams A, B, C, D and E participate, and each team has to play with another team. Table given below shows the schedule of the tournament. Total allotted over for one team to bat is 50 overs.
The formula is given to calculate the run rate of a team in a particular match and net run rate of a team:
Run rate if they didn’t lose all 10 wickets = Total runs scored/Total overs faced
(OR)
Run rate if they lose all 10 wickets = Total runs scored/50
Net run rate = Run rate of the team + Run rate against another team
Note: Net run rate of both the teams in a particular match will be same (magnitude wise) while the net run rate of losing team will be negative while the net run rate of winning team will be positive in that match.
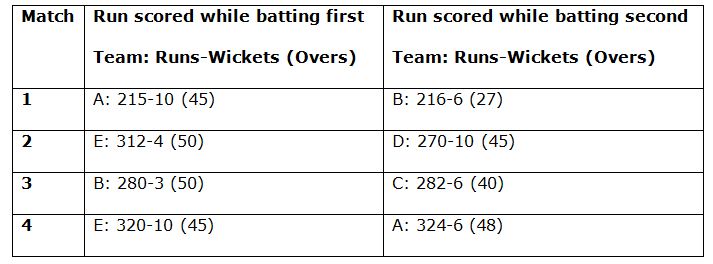
1) Table given below shows the run scored in first four matches, then what will be the sum of total net run rate of teams B, C and E together?
a) 3.79
b) 3.35
c) 3.84
d) 4.19
e) None of these
2) If team C batted first in the 5th and 10th match and scored 292 and 308 in its full quota of 50 overs. 5th match, C won by 52 runs in which D batted for 50 overs. 10th match C lost the match, in which team E chased the target in 48 overs and scored 4 runs more than team C, then what is the ratio of magnitude of net run rate of team C in 5th match to that in 10th match?
a) 52: 17
b) 3: 2
c) 17: 5
d) 48: 13
e) None of these
3) If the net run rate of team B in 7th match is ‘-0.5’, in which difference between runs scored by both the team is 5 runs. If team B scored 225 runs after losing all its 10 wickets, then in how many overs did team E chased that target?
a) 43 overs
b) 42.4 overs
c) 46 overs
d) 48.2 overs
e) None of these
4) Net run rate of team A after 6th match is 2.8 and to qualify for the next stage its net rate should be 4.6. While batting first in 8th match team C scored 350 runs in his full quota of 50 overs, then to qualify for the next stage in how many overs team A should chase that target if team A scored 352 runs?
a) 40 overs
b) 35 overs
c) 45 overs
d) 42.5 overs
e) None of these
5) While batting first in 9th match team D scored 224 runs after losing all 10 wickets in 42 overs and if team B chased that target in 38 overs and scored 228 runs, then what is the per centincrement in the net run rate of team B after the 9th match if before 9th match net run rate of team B was 4?
a) 38%
b) 32%
c) 42%
d) 46%
e) None of these
Direction (6 – 10): Study the following data carefully and answer the questions:
There are total five airlines P, Q, R, S and T by which a person can book his flight ticket. The fare of a airlines depends on base fare, taxes/surcharge and convenience fee as given below:
Total fare = Base fare + Taxes/Surcharge + Convenience fee
Taxes/Surcharge = 25% of Base fare
Convenience fee for one – way = 10% of Base fare + 20% of Taxes/Surcharge
Base fare for round trip = One – way base fare + Rs.908
Convenience fee for round trip = 15% of Base fare + 30% of Taxes/Surcharge
Base fare for each airline is different and based on the distance between origin and destination. Table given below shows the base fare calculator of those different airlines: 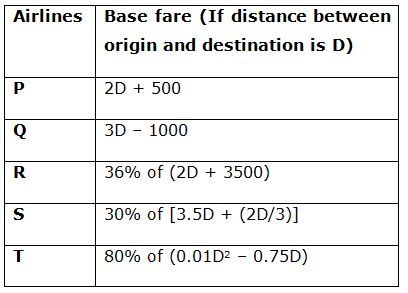
6) If Ramesh goes from Kolkata to Agra by airlines P and comes back by airlines Q and distance between Kolkata and Agra is 1200 km, then what is difference between his total fare from Kolkata to Agra and that from Agra to Kolkata?
a) Rs.420
b) Rs.380
c) Rs.640
d) Rs.560
e) None of these
7) Two employees A and B goes from Bangalore to Chennai for some office meeting and travel expense is given by the company. A goes by Q and B goes by R, then what is the total reimbursement made by the company to both the employees if the distance between Bangalore to Chennai is 750 km?
a) Rs.3580
b) Rs.4270
c) Rs.4830
d) Rs.3670
e) None of these
8) What is the difference between total fare amount for Mohan and that for Rohan when both travels round trip between A and B. Mohan goes by P and comes back by Q while Rohan goes by R and comes back by the same airlines? Assume distance between A and B is 600 km.
a) Rs.225
b) Rs.445
c) Rs.335
d) Rs.285
e) None of these
9) Ashok goes from Delhi to Goa for vacation by airlines R and comes to Delhi by airlines S. If distance between Delhi to Goa is 2000 km, then fare from Delhi to Goa is what per cent more than that from Goa to Delhi?
a) 12%
b) 8%
c) 16%
d) 18%
e) None of these
10) Mukesh goes from Hyderabad to Bangalore by airlines T and total fare amount for Mukesh is Rs.3528, then what is the distance between Hyderabad and Bangalore?
a) 700 km
b) 550 km
c) 625 km
d) 600 km
e) None of these
Answers :
Direction (1-5) :
1) Answer: d)
Net run rate of team A after its first match = (215/50) – (216/27) = -3.7
Net run rate of team B after its first match = (216/27) – (215/50) = 3.7
Net run rate of team A after its second match = -3.7 + [(324/48) – (320/50)]
= -3.35
Net run rate of team B after its second match = 3.7 + [(280/50) – (282/40)]
= 2.25
Net run rate of team C after its first match = (282/40) – (280/50) = 1.45
Net run rate of team D after its first match = (270/50) – (312/50) = -0.84
Net run rate of team E after its first match = (312/50) – (270/50) = 0.84
Net run rate of team E after its second match = 0.84 + [(320/50) – (324/48)]
= 0.49
Sum of total net run rate of teams B, C and E together = 2.25 + 1.45 + 0.49
= 4.19
2) Answer: a)
Runs scored by team D in 5th match = 292 – 52 = 240
Runs scored by team E in 10th match = 308 + 4 = 312
Net run rate of team C in 5th match = (292/50) – (240/50) = 1.04
Net run rate of team C in 10th match = (308/50) – (312/48) = -0.34
Required ratio = 1.04: 0.34 = 52: 17
3) Answer: c)
Since, team E chased the target. So, team E won the match against team B in 7th match.
Runs scored by team E = 225 + 5 = 230
Let in ‘x’ overs in team E chased that target.
Now,
Net run rate of team B in 7th match =(225/50) – (230/x) = -0.5
4.5 + 0.5 = 230/x
x = 46
4) Answer: a)
Required run rate for team A in 8th match = 4.6 – 2.8 = 1.8
Let in ‘x’ overs team A chased that target.
Now,
(352/x) – (350/50) = 1.8
352/x = 8.8
x = 40
5) Answer: a)
Run rate of team D in 9th match = 224/50 = 4.48
Run rate of team B in 9th match = 228/38 = 6
Net run rate of team B after 9th match = 6 – 4.48 = 1.52
Required per cent increment = (1.52/4) * 100 = 38%
Direction (6-10) :
6) Answer: a)
Base fare between Kolkata and Agra by airlines P = 2D + 500 = Rs.2900
Base fare between Kolkata and Agra by airlines Q = 3D – 1000 = Rs.2600
Total fare from Kolkata to Agra = 2900 + 25% of 2900 + 10% of 2900 + 20% of 25% of 2900 = 2900 + 725 + 290 + 145 = Rs.4060
Total fare from Agra to Kolkata = 2600 + 25% of 2600 + 10% of 2600 + 20% of 25% of 2600 = 2600 + 650 + 260 + 130 = Rs.3640
Required difference = 4060 – 3640 = Rs.420
7) Answer: b)
Base fare of A from Bangalore to Chennai by airlines Q = 3D – 1000 = Rs.1250
Base fare of B from Bangalore to Chennai by airlines R = 80% of (2D + 3500) = Rs.1800
Total fare from Bangalore to Chennai = 1250 + 25% of 1250 + 10% of 1250 + 20% of 25% of 1250 = 1250 + 312.5 + 125 + 62.5 = Rs.1750
Total fare from Bangalore to Chennai = 1800 + 25% of 1800 + 10% of 1800 + 20% of 25% of 1800 = 1800 + 450 + 180 + 90 = Rs.2520
Total reimbursement made by the company to both the employees = 1750 + 2520 = Rs.4270
8) Answer: c)
Base fare of A to B by airlines P = 2D + 500 = Rs.1700
Base fare of A to B by airlines Q = 3D – 1000 = Rs.800
Base fare of A to B by airlines R = 36% of (2D + 3500) = Rs.1692
Base fare of A to B = 1692 + 908 = Rs.2600
Total fare of Mohan when he goes from A to B = 1700 + 25% of 1700 + 10% of 1700 + 20% of 25% of 1700 = 1700 + 425 + 170 + 85 = Rs.2380
Total fare of Mohan when he goes from B to A = 800 + 25% of 800 + 10% of 800 + 20% of 25% of 800 = 800 + 200 + 80 + 40 = Rs.1120
Total fare of Rohan when he goes from A to B and comes back to A = 2600 + 25% of 2600 + 15% of 2600 + 30% of 25% of 2600 = 2600 + 650 + 390 + 195 = Rs.3835
Required difference ratio = (2380 + 1120) ~ 3835 = Rs.335
9) Answer: b)
Base fare from Delhi to Goa by airlines R = 36% of (2D + 3500) = Rs.2700
Base fare from Goa to Delhi by airlines S = 30% of [3.5D + (2D/3)] = Rs.2500
Total fare from Delhi to Goa = 2700 + 25% of 2700 + 10% of 2700 + 20% of 25% of 2700 = 2700 + 675 + 270 + 135 = Rs.3780
Total fare from Goa to Delhi = 2500 + 25% of 2500 + 10% of 2500 + 20% of 25% of 2500 = 2500 + 625 + 250 + 125 = Rs.3500
Required per cent = [(3780- 3500)/3500] * 100 = 8%
10) Answer: d)
Let the distance between Hyderabad and Bangalore = ‘D’ km
Base fare from Hyderabad to Bangalore by airlines T = 80% of (0.01D2 – 0.75D) = (0.008D2 – 0.6D)
Total fare from Hyderabad to Bangalore = (0.008D2 – 0.6D) + 25% of (0.008D2 – 0.6D) + 10% of (0.008D2 – 0.6D) + 20% of 25% of (0.008D2 – 0.6D) = 3528
140% of (0.008D2 – 0.6D) = 3528
(0.008D2 – 0.6D) = 2520
D = 600 km





