SBI PO 2019 Notification is about to come and it is the most awaited exam among the aspirants. We all know that new pattern questions are introducing every year in the SBI PO exam. Further, the questions are getting tougher and beyond the level of the candidate’s expectations.
Our IBPS Guide is providing High-Level New Pattern Quantitative Aptitude Questions for SBI PO 2019 so the aspirants can practice it on a daily basis. These questions are framed by our skilled experts after understanding your needs thoroughly. Aspirants can practice these high-level questions daily to familiarize with the exact exam pattern. We wish that your rigorous preparation leads you to a successful target of becoming SBI PO.
[WpProQuiz 4721]
Click here to View Quantitative Aptitude Questions in Hindi
Direction (1 – 5): Study the following information carefully and answer the given questions:
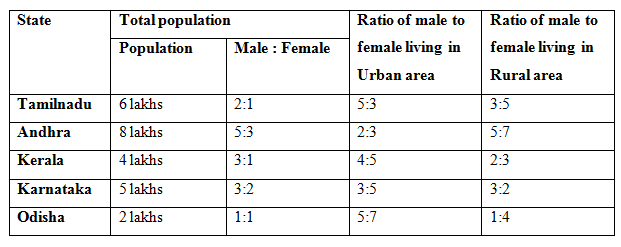
1) What is the percentage of the population living in urban area having the age below 30 years out of the total population of Tamilnadu?
Statement I: If the age of 45% male and 50% female living in urban area of Tamilnadu is below 30 years.
Statement II: If the 60% of the total population of Tamilnadu living in urban area.
a) Only I
b) Only II
c) Either I or II sufficient
d) All I and II necessary to answer the question
e) The question can’t be answered even with all I and II
2) Quantity I: If 90% of the population of Kerala living in urban area, then what is the sum of the male population in rural area and the female population in urban area?
Quantity II: What is the difference between the female population of Karnataka and the female population of Andhra?
a) Quantity I > Quantity II
b) Quantity I ≥ Quantity II
c) Quantity II > Quantity I
d) Quantity II ≥ Quantity I
e) Quantity I = Quantity II or Relation cannot be established
3) Quantity I: The urban population of Andhra is 60 %. Out of the urban population of Andhra, 30% and 45% of the urban male and female is illiterate respectively. Then find the sum of the rural population of Andhra and the literate population of urban area?
Quantity II: What is the sum of the total population of Odisha and the female population of Karnataka?
a) Quantity I > Quantity II
b) Quantity I ≥ Quantity II
c) Quantity II > Quantity I
d) Quantity II ≥ Quantity I
e) Quantity I = Quantity II or Relation cannot be established
4) If 30%, 40%, 20%, 40% and 50% of the population lives in the rural area of Tamilnadu, Andhra, Kerala, Karnataka and Odisha respectively. Which of the following statement is correct?
Statement I: The urban male population of Tamilnadu is equal to the urban female population of Andhra.
Statement II: Rural female population of Karnataka is equal to the Rural female population of Odisha.
Statement III: Rural population of Karnataka is equal to the sum of the rural population of Tamilnadu and the rural male population of the Odisha together.
a) Only I
b) Only II
c) Only III
d) Both I and II
e) Both II and III
5) What is the difference between total male population of all the states together and total of the female population of all the states together?
a) 6 lakhs
b) 7 lakhs
c) 9 lakhs
d) 5 lakhs
e) None of these
Direction (6 – 10): Study the following information carefully and answer the given questions:
The Pie-chart shows the market share of mobiles sold by different companies in the year 2016.
The line graph shows the sales of Apple for the given period.
6) Quantity I: If the market share of sales in 2017 is increased by 30% of the percentage share in 2016, then find the sale of Nokia in the year 2017, if the total value of all companies in 2017 is 60 lakhs?
Quantity II: If the market share of sales in 2014 is same as that in 2016, then find the sale of Moto in the year 2014?
a) Quantity I > Quantity II
b) Quantity I ≥ Quantity II
c) Quantity II > Quantity I
d) Quantity II ≥ Quantity I
e) Quantity I = Quantity II or Relation cannot be established
7) Quantity I: What is the average sale of Apple in the given period?
Quantity II: What is average sale of Samsung, Vivo and Oppo in 2016?
a) Quantity I > Quantity II
b) Quantity I ≥ Quantity II
c) Quantity II > Quantity I
d) Quantity II ≥ Quantity I
e) Quantity I = Quantity II or Relation cannot be established
8) If the market share of 2016 is equal to the market share of 2017.
Quantity I: What is the difference between the sale of Oppo and Nokia?
Quantity II: What is the difference between the sale of Samsung and Vivo?
a) Quantity I > Quantity II
b) Quantity I ≥ Quantity II
c) Quantity II > Quantity I
d) Quantity II ≥ Quantity I
e) Quantity I = Quantity II or Relation cannot be established
9) Quantity I: The sale of Apple in 2017 is what percent of the sale of Moto in 2016?
Quantity II: The sale of Samsung in 2016 is what percent of the sale of Nokia in 2016?
a) Quantity I > Quantity II
b) Quantity I ≥ Quantity II
c) Quantity II > Quantity I
d) Quantity II ≥ Quantity I
e) Quantity I = Quantity II or Relation cannot be established
10) Quantity I: What is the average sale of Nokia, Apple, Samsung, Moto, Vivo and Oppo in 2016?
Quantity II: If the market share of all the companies in 2018 is increases by 10% of the percentage share in 2016, then find the average sale of all the companies in 2018?
a) Quantity I > Quantity II
b) Quantity I ≥ Quantity II
c) Quantity II > Quantity I
d) Quantity II ≥ Quantity I
e) Quantity I = Quantity II or Relation cannot be established
Answers:
Direction (1 – 5):
1) Answer: d)
From Statement I,
Given data is not sufficient to the answer the question.
So, Statement I alone is not sufficient to the answer the question.
From Statement II,
Urban population = (60/100)*6 = 3.6 lakhs
Rural population = (40/100)*6 = 2.4 lakhs
So, Statement II alone is not sufficient to the answer the question.
From I and II,
Urban Male = (5/8)*3.6 lakhs = 2.25 lakhs
Urban female = (3/8)*3.6 lakhs = 1.35 lakhs
Below 30 male = (45/100)*2.25 lakhs = 101250
Below 30 female = (50/100)*1.35 lakhs = 67500
Total of below 30 = 101250 + 67500 = 168750
Required percentage = (168750/600000)*100 = 28.125%
2) Answer: a)
From quantity I,
Urban population = (90/100)*4 lakhs = 3.6 lakhs
Female population in urban= (5/9)*3.6 = 2 lakhs
Rural population = (10/100)*4 lakhs = 40000
Male population in rural = (2/5)*40000 = 16000
Sum=200000 + 16000 = 216000 = 2.16 lakhs
From quantity II,
Karnataka female population = (2/5)*5=2 lakhs
Female population in Andhra = (3/8)*8=3 lakhs
Difference = 3 – 2 = 1 lakh
Quantity I > Quantity II
3) Answer: a)
From quantity I,
Urban population of Andhra = (60/100)*8 = 4.8 lakhs
Urban male = (2/5)*4.8 = 1.92 lakhs
Literate male = (70/100)*1.92 lakhs = 1.344 lakhs
Urban female = (3/5)*4.8 = 2.88 lakhs
Literate female = (55/100)*2.88 = 1.584 lakhs
Literate urban = 1.344 + 1.584 = 2.928 lakhs
Rural = (40/100)*8 = 3.2 lakhs
Sum = 2.928 + 3.2 = 6.128 lakhs
From quantity II,
Female of Karnataka = (2/5)*5 = 2 lakhs
Odisha = 2 lakhs
Sum = 2 + 2 = 4 lakhs
Quantity I > Quantity II
4) Answer: b)
Tamilnadu:
Male = 4 lakhs
Female = 2 lakhs
Urban = (70/100)*6 = 4.2 lakhs
Urban male = (5/8)*4.2 = 2.625 lakhs
Urban female = (3/8)*4.2 = 1.575 lakhs
Rural = (30/100)*6 = 1.8 lakhs
Rural male = (3/8)*1.8 = 67500
Rural female = (5/8)*1.8 = 112500
Andhra:
Male=5 lakhs
Female=3 lakhs
Urban population = (60/100)*8 = 4.8 lakhs
Urban male = (2/5)*4.8 = 1.92 lakhs
Urban female = (3/5)*4.8 = 2.88 lakhs
Rural population = (40/100)*8 = 3.2 lakhs
Kerala:
Male=3 lakhs
Female=1 lakhs
Urban population= (80/100)*4 = 3.2 lakhs
Rural population= (20/100)*4 = 80000
Karnataka:
Male = 3 lakhs
Female = 2 lakhs
Urban population = (60/100)*5 = 3 lakhs
Urban male = (3/8)*3 = 1.125 lakhs
Urban female = (5/8)*3 = 1.875
Rural population= (40/100)*5 = 2 lakhs
Rural male = (3/5)*2 lakhs = 1.2 lakhs
Rural female = (2/5)*2= 80000
Odisha:
Male = 1 lakh
Female = 1 lakh
Urban population = 1 lakh
Rural population=1 lakh
Rural male = (1/5)*1= 20000
Rural female = (4/5)*1= 80000
5) Answer: b)
Tamilnadu:
Male=4 lakhs
Female=2 lakhs
Andhra:
Male=5 lakhs
Female=3 lakhs
Karnataka:
Male=3 lakhs
Female=2 lakhs
Kerala:
Male=3 lakhs
Female=1 lakhs
Odisha:
Male=1 lakhs
Female=1 lakhs
Total of male population=4+5+3+3+1=16 lakhs
Total female population=2+3+2+1+1=9 lakhs
Difference=16-9=7 lakhs
Direction (6 – 10):
6) Answer: a)
From Quantity I,
Share of sales 2017 in Nokia = (20/100)*(130/100) = 26/100 = 26%
Sale of Nokia = (26/100)*60 = 15.6 lakhs
From Quantity II,
Market share of Apple in 2016 is 18%. This will be so in 2014 also.
Sale of Moto = 12*(4/18) = 2.66 lakhs
Quantity I > Quantity II
7) Answer: c)
From quantity I,
Average = (6+4+9+10+12)/5 = 8.2 lakhs
From quantity II,
Sales of Samsung in 2016 = (9/18)*25 = 12.5 lakhs
Vivo in 2016 = (9/18)*15 = 7.5 lakhs
Oppo in 2016 = (9/18)*10 = 5 lakhs
Average = (12.5+7.5+5)/3 = 8.33 lakhs
Quantity II > Quantity I
8) Answer: e)
From quantity I,
Sale of Oppo = (9/18)*10 = 5lakhs
Sale of Nokia = (9/18)*20 = 10lakhs
Difference = 10 – 5 = 5 lakhs
From quantity II,
Sale of Samsung = (9/18)*25 = 12.5 lakhs
Sale of Vivo = (9/18)*15 = 7.5 lakhs
Difference = 12.5 – 7.5 = 5 lakhs
Quantity I = Quantity II
9) Answer: a)
From quantity I,
Apple 2017=10
Moto 2016 = (9/18)*12 = 6 lakhs
Required percentage = (10/6)*100 = 500/3 %
From quantity II,
Samsung 2016 = (9/18)*25=12.5lakhs
Nokia in 2016 = (9/18)*20=10lakhs
Required percentage = (12.5/10)*100 = 125 %
Quantity I > Quantity II
10) Answer: c)
From quantity I,
Nokia in 2016 = (9/18)*20=10 lakhs
Apple in 2016 = (9/18)*18=9 lakhs
Samsung in 2016 = (9/18)*25=12.5 lakhs
Moto in 2016 = (9/18)*12=6 lakhs
Vivo in 2016 = (9/18)*15=7.5 lakhs
Oppo in 2016 = (9/18)*10=5 lakhs
Average = (10 + 9 + 12.5 + 6 + 7.5 + 5)/6 = 8.33 lakhs
From quantity II,
Nokia 2018 = 20*(110/100) = 22 %
Apple 2018 = 18*(110/100) = 19.8 %
Samsung in 2018 = 25*(110/100) = 27.5 %
Moto in 2018 = 12*(110/100) = 13.2 %
Vivo in 2018 = 15*(110/100) = 16.5 %
Oppo in 2018 = 10*(110/100) = 11 %
Sale of Nokia 2018 = (12/19.8)*22 = 44/3.3 lakhs
Sale of Apple in 2018 = 12 lakhs
Sale of Samsung = (12/19.8)*27.5 = 55/3.3
Sale of Moto = (12/19.8)*13.2 = 8 lakhs
Sale of Vivo = (12/19.8)*16.5 = 10 lakhs
Sale of Oppo = (12/19.8)*11 = 22/3.3 lakhs
Average = (44/3.3 + 12 + 55/3.3 + 8 + 10 + 22/3.3)/6 = 11.11 lakhs
Quantity II > Quantity I
Daily Practice Test Schedule | Good Luck
| Topic | Daily Publishing Time |
| Daily News Papers & Editorials | 8.00 AM |
| Current Affairs Quiz | 9.00 AM |
| Current Affairs Quiz (Hindi) | 9.30 AM |
| IBPS SO/NIACL AO Prelims – Reasoning | 10.00 AM |
| IBPS SO/NIACL AO Prelims – Reasoning (Hindi) | 10.30 AM |
| IBPS SO/NIACL AO Prelims – Quantitative Aptitude | 11.00 AM |
| IBPS SO/NIACL AO Prelims – Quantitative Aptitude (Hindi) | 11.30 AM |
| Vocabulary (Based on The Hindu) | 12.00 PM |
| IBPS SO/NIACL AO Prelims – English Language | 1.00 PM |
| SSC Practice Questions (Reasoning/Quantitative aptitude) | 2.00 PM |
| IBPS Clerk – GK Questions | 3.00 PM |
| SSC Practice Questions (English/General Knowledge) | 4.00 PM |
| Daily Current Affairs Updates | 5.00 PM |
| SBI PO/IBPS Clerk Mains – Reasoning | 6.00 PM |
| SBI PO/IBPS Clerk Mains – Quantitative Aptitude | 7.00 PM |
| SBI PO/IBPS Clerk Mains – English Language | 8.00 PM |
This post was last modified on August 12, 2019 12:05 pm